As the Finance Minister of India , Mr. Arun Jaitley, got up to deliver the Union Budget for the Financial Year 2017-2018, every Business Man in the country was waiting for the Tax Reforms. The Direct Tax Reforms given in the budget dated 1st Feb’2017 will be applicable in the F.Y. 2017-18 or A.Y 2018-19. Some crucial and evident changes have been made by the Government for the Small and Medium Scale Business in the budget.
As per the Narendra Modi Government, the Tax Revenue of the central Government from Direct Tax Collection has gone up by 17% in F.Y. 2015-16 as compared to F.Y. 2014-15, and the rate of growth in advance tax in personal income tax domains for the F.Y. 2016-17 has increased by 34.81% till 20th Jan’2017 as compared to F.Y 2015-16.
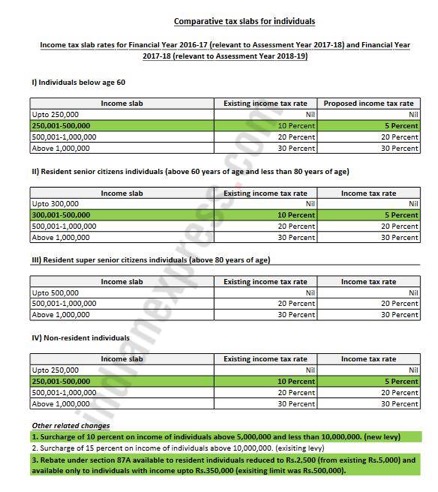
We have decoded the key changes proposed in the Union Budget announced by the Finance Minister on February 1, 2017.
- Tax slabs
It has been proposed to reduce the tax rate for taxable income less than Rs 500,000 from current 10% to 5% benefiting Individuals (resident/ non-resident) below the age of 60 years and Individuals (resident/ non-resident) above the age of 60 years and below the age of 80 years.
- Rebate under section 87A
Rebate under section 87A of the Income-tax Act, 1961 (“the Act”) is proposed to be reduced from Rs 5,000 to Rs 2,500. It has also been proposed to restrict such rebate to resident individuals whose total income does not exceed Rs 350,000 (earlier Rs 500,000). Considering the above amendments, the net benefit arising to an individual with taxable income of Rs 350,000 and Rs 500,000 is Rs 2,575 and Rs 7,725 respectively.
- Partial exemption for pension
The existing provision of section 10(12A) of the Act provides that payment from National Pension System (“NPS”) trust to an employee on closure of his account or opting out shall be exempt up to 40% of total amount payable to him. In order to provide relief to an employee who is a subscriber of NPS, it is proposed to provide exemption for partial withdrawal not exceeding 25% of the contribution made by an employee in accordance with the terms and conditions specified under Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 2013 and regulations made thereunder.
ALSO READ: Union Budget 2017: Railways get Rs 55000-crore boost, will have better safety, no fare hikes
- Rationalization of deduction under section 80CCD for self-employed individual
In order to bring about parity between an individual who is an employee and an individual who is self-employed, it is proposed to amend section 80CCD of the Act so as to increase the upper limit of 10% of Gross Total Income (“GTI”) to 20% in case of individual who is self-employed. Accordingly, for a self-employed individual, contributions to NPS to the extent of 20 percent of his/ her GTI will now be allowed.
- Withholding tax obligation for individual not liable to tax audit
As per the existing provision of the Act, withholding tax obligation on rent payments arises only in case of individuals or HUF who are liable to tax audit. It is proposed that individual or HUF not liable for tax audit will now be required to withhold tax at the rate of 5%, if the rent exceeds Rs 50,000 per month or part of month on payment of rent.
Also Tax deduction and collection Account Number (“TAN”) will not be required to be obtained.
Further, tax would be required to be withheld only once during the previous year in the last installment payable for the year.
In addition to the above, it is proposed that under section 206AA of the Act, maximum deduction shall not exceed the rent payable for the last month of the previous year/ last month of tenancy.
- Shifting base year from 1981 to 2001 for computation of capital gains:
Existing provisions gave the assesse an option to consider Fair Market Value (“FMV”) as on April 1, 1981 for capital assets acquired before the said date. It has been proposed to shift the base to April 1, 2001. Accordingly assesses have an option to consider cost or FMV as on April 1, 2001 as their cost in respect of assets acquired on or before April 1, 2001.
Further, for the purpose of computing indexed cost of acquisition, 2001 shall be considered as the base year.
- Reduction of holding period for computation of capital gains for immovable property:
It is proposed to amend section 2(42A) of the Act to reduce the holding period from existing 36 months to 24 months in case of immovable property being land and building or both to quality as long term capital asset.
- Expansion of scope of long term bonds under section 54EC
It is proposed to provide exemption under section 54EC of the Act on investment of long term capital gains in any bond redeemable after three years that shall be notified by the central government. This will be in addition to investments in NHAI bonds and RECL bonds where exemption was allowed on investment up to Rs 5,000,000.
- Measures for promoting digital payments in case of presumptive business income cases
In order to promote digital transactions and to encourage small unorganized business to accept digital payments, it is proposed to amend section 44AD of the Act to reduce the existing rate of deemed total income of 8% to 6% in respect of turnover or gross receipts received by an account payee cheque or account payee bank draft or use of electronic clearing system through a bank account during the previous year or before the due date specified in sub-section (1) of section 139 in respect of that previous year. However, the existing rate of deemed profit of 8% referred to in section 44AD of the Act, shall continue to apply in respect of total turnover or gross receipts received in any other mode.
For more information on Tax Reforms, feel free to reach us on, info@gapeseedconsulting.com or call +91-9599444639/+91-9599444630
More Newsletter
Most important Income tax changes which will occur from 1st April
Gapeseed’s Accounting Services for Small Businesses
Outsource Bookkeeping Services and Simplify Taxation
FRRO and Taxation Services for Expats in India

