Income Tax Return is defined under Section 139(1) of the Income Tax Act, where an Income Tax Return is required to be submitted by every Individual where his income exceeds the minimum income chargeable to Income Tax.
E-filing or electronic filing is submitting your income tax returns online, using tax preparation software that has been pre-approved by the relevant tax authority.
WHO IS REQUIRED TO FILE INCOME TAX RETURN?
- An individual, if gross total income (before allowing any deductions under section 80C to 80U) exceeds Rs 2,50,000/-.
- There is a limit ofRs 3,00,000 for senior citizens ( who are more than 60 years old but less than 80 years old) or Rs 5,00,000 for super senior citizens (who are more than 80 years old).
- A company irrespective of whether there is any income or loss or NILincome during the financial year, it is mandatory to file income tax return.
- A firm irrespective of whether there is any income or loss or NIL income during the financial year, it is mandatory to file income tax return.
- E-filing of Income Tax return is compulsory if you want to claim income tax refund.
- If one wants to carry forward loss under any head of income, it is mandatory to file IT Return.
- Return filing is mandatory if you are a Resident individual and have an asset or financial interest in an entity located outside of India.
- One is required to file an income tax return when you are in receipt of income derived from property held under a trust for charitable or religious purposes or a political party or a research association, news agency, educational or medical institution, trade union, a not for profit university or educational institution, a hospital, infrastructure debt fund, any authority, body or trust.
- If tax has been deducted from your income, then you must file income tax return to avoid notice from the income tax department as it has information about your income.
PROCESS OF FILING INCOME-TAX RETURN
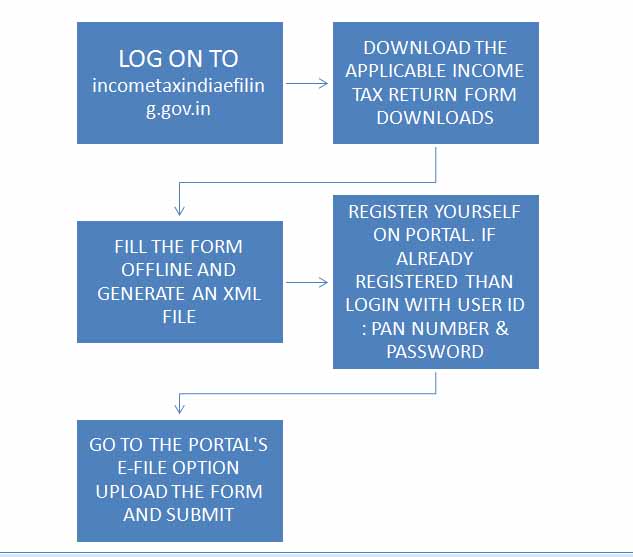
- For any queries and any FAQs while filing Income tax return please feel free to contact Gapeseed Consulting Pvt. Ltd.
TYPES OF FORMS FOR DIFFERENT ASSESSEES
| FORM | SOURCE OF INCOME | DUE DATES FOR FILING |
| ITR-1(SAHAJ) | · INCOME FROM SALARY
· OTHER INCOME SUCH AS INTEREST · INCOME FROM ONE HOUSE PROPERTY |
· 31ST JULY |
| ITR-2 FOR INDIVIDUALS AND HUFs | · INCOME FROM SALARY
· OTHER INCOME SUCH AS INTEREST · INCOME FROM ONE HOUSE PROPERTY · INCOME FROME CAPITAL GAINS · INCOME FROM BUSINESS OR PROFESSION FOR HUFs, INDIVIDUALS AND PARTNERSHIPS |
· 31ST JULY |
| ITR-3 FOR INDIVIDUALS AND HUFs | · INCOME FROM BUSINESS | · 31ST JULY |
| ITR-4 (SUGAM) | · INCOME FROM SALARY/PENSION
· BUSINESS INCOME WHERE INCOME COMPUTED ON PRESUMPTIVE INCOME BASIS · INCOME FROM NOT MORE THAN ONE HOUSE PROPERTY · INCOME FROM OTHER SOURCES |
· 31ST JULY |
| ITR-6 | · INCOME OF COMPANIES | · 30TH SEPTEMBER |
| ITR-7 | · INCOME OF CHARITABLE AND RELIGIOUS INSTITUTE
· INCOME OF POLITICAL PARTY · PERSONS CLAIMING EXEMPTIONS UNDER SECTION 10. · INCOME OF UNIVERSITY, COLLEGE OR INSTITUTION. |
· 30TH SEPTEMBER
|
CONSEQUENCES OF NON-FILING OF RETURNS
Filing of Income Tax Returns helps an Individual to establish a standard proof of Income with the Income tax department. But there are certain consequences of Non-filing: –
- Losses of business or profession and capital loss cannot be carried forward in the next year if one fails to file an income tax return for the same year.
- Due to Non filing of return the assessee has to bear a penalty of Rs. 5000.
- The Assessee will also be liable to charge Interest @ 1% for non-filing of return.
- Company assesses are liable to prosecution as well in case of non-disclosure of income and non-filing of Income tax return.